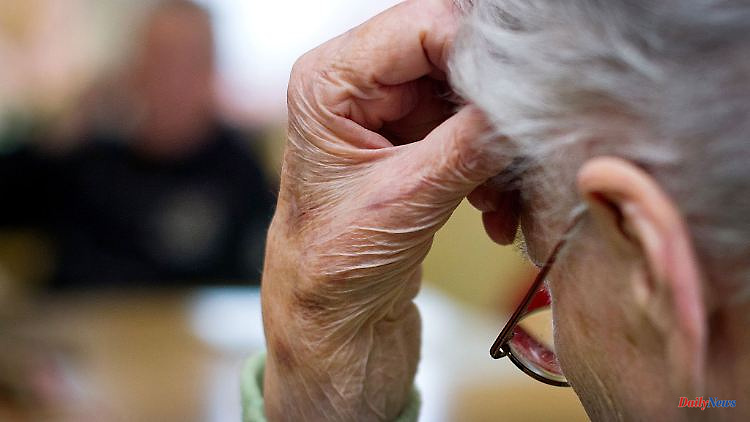
A new Alzheimer's drug has been approved in the United States for the second time since 2021 - an important advance in the treatment of dementia. But the euphoria is limited, because the approval study indicates serious side effects such as cerebral hemorrhage.
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved a new drug for the treatment of Alzheimer's. The FDA said the drug, to be marketed under the Leqembi name, represents "an important advance toward effective Alzheimer's treatment." The drug is FDA-recommended for use in patients with early-stage neurodegenerative disease.
In its statement, the agency referred to preliminary data from a study published in September that showed Leqembi slowed cognitive decline in Alzheimer's patients by 27 percent over an 18-month period. However, the same study had also pointed out serious side effects.
Some of the patients treated suffered cerebral hemorrhage. In addition, at least one person who received the treatment died. In its approval, the FDA included a warning about possible bleeding in the drug information.
Leqembi, whose active ingredient is called lecanemab, targets deposits of a protein called beta-amyloid. The cause of Alzheimer's disease is not yet fully understood. What is certain, however, is that amyloid deposits form around the neurons in the brains of the patients, destroying them over time. This process causes the memory loss characteristic of Alzheimer's. The FDA's approval of Leqembi is based on the results of clinical studies, according to which the drug reduces amyloid deposits.
Leqembi is the second Alzheimer's drug to receive FDA approval since 2021. In June 2021, the authority gave the green light for the Aduhelm drug, which is based on an active ingredient called aducanumab.
After Aduhelm's approval, there was considerable controversy over proving its effectiveness. As a result of the approval, three high-ranking FDA officials resigned, and the agency later restricted its use. An investigative report by the US Congress also criticized the extremely high price of 56,000 US dollars per year for Aduhelm.
Aduhelm and Leqembi were approved by the FDA in an accelerated process. This allows the drug agency to expedite medications for serious conditions without treatments already approved.
Alzheimer's is the most common form of dementia. The disease of the brain leads to the loss of mental functions such as thinking, language, judgment and orientation and to the death or severe damage to brain cells, especially in the cerebral cortex. The ability to socialize is also lost.